Imagine you’re managing a team but have no clue about how well everyone is performing. Without a clear set of indicators, it’s tough to tell if your team is on track or veering off course.
If you don’t measure and analyze each relevant data point, it’s difficult to gauge the success of your strategies. That’s exactly where key performance indicators (KPIs) come into play.
KPIs are essential tools for meticulously tracking individual and team performance.
By setting clear KPIs, you can see precisely where you’re excelling and where you need to pivot.
In fact, about 38% of organizations already use KPIs to manage and track performance-related goals. This reflects a growing reliance on structured, measurable metrics that offer clear benchmarks for success.
It makes managing a team more than just a guessing game—it turns it into a strategic mission. Let’s explore how KPIs empower you to make informed decisions and drive your team towards success.
What Is KPI?
A quantifiable value that shows how well people or organizations are accomplishing their main goals is called a key performance indicator, or KPI. Organizations use KPIs at several levels to assess how well they are accomplishing their goals.
High-level KPIs may focus on the overall performance of the enterprise, while low-level KPIs might concentrate on processes in departments such as sales, marketing, HR, or support.
For instance, a software company aiming to be the fastest-growing entity in its sector might view year-over-year (YOY) revenue growth as its primary KPI.
On the other hand, a retail chain may find that same-store sales figures are the most relevant metric for measuring its growth. Utilizing KPIs is based on the rigorous process of data collection, storage, cleaning, and synthesis.
This data can be financial or non-financial and may pertain to any aspect of a company’s operations. The ultimate goal of KPIs is to provide a clear, concise picture of performance across all levels of the organization, enabling management to make informed strategic decisions.
Difference Between KPIs and Metrics
Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics are both essential tools in business analytics but serve distinct purposes. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between KPIs and metrics:
| Aspect | KPI (Key Performance Indicator) | Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | KPIs are used to measure performance against a specific business objective. | Metrics are standard measurements used to gauge specific aspects of business performance. |
| Impact | KPIs have a direct correlation with strategic goals and are critical for decision-making. | Metrics provide insights but may not be directly tied to the overarching business strategy. |
| Usage | KPIs are carefully selected to reflect the critical success factors of an organization. | Metrics can be numerous and varied, providing detailed data on various business operations. |
| Examples | For a tech startup, a KPI might be monthly recurring revenue (MRR) or customer acquisition cost (CAC). | An example of a metric could be the number of website visitors or average session duration. |
| Decision-making | Management often uses KPIs to make strategic decisions and assess whether organizational goals are being met. | Metrics may inform more tactical decisions and day-to-day operations management. |
Suggested Read:
OKRs vs KPIs: What’s The Difference?
Why Are KPIs Important?
Key Performance Indicators, or KPIs, are like the dashboard in your car—they show you what’s working well and what needs a tune-up to ensure you’re on the right path toward your business goals.
1. Enables data-driven decisions
KPIs help everyone in your team understand the direction and keep all efforts aligned with your main objectives. When you know what you’re aiming for, it’s much easier to hit the target.
KPIs also provide the hard numbers, giving you the clarity to make informed decisions. This means you can back up your choices with data and really know why you’re doing what you’re doing.
2. Provides performance visibility
Visibility is key in any game, right? KPIs lay it all out on the table, showing which parts of your business are performing well and which might be lagging behind. This transparency helps you pinpoint where you need to improve.
3. Optimizes resource allocation
By highlighting what’s working and what isn’t, KPIs allow you to distribute resources smartly. Put more fuel where it’s needed and trim down on areas that aren’t yielding much. It’s all about getting the most out of what you have.
4. Enhances motivation and accountability
When everyone knows the score and what counts is clear, it drives motivation. People step up their game. KPIs make it easy to set clear expectations so everyone knows what success looks like and owns their part in getting there.
Types of KPIs
Broadly, KPIs can be classified into three main categories: Strategic, Operational, and Functional. Let’s take a brief look into it:
1. Strategic KPIs
These are the big-picture indicators. Strategic KPIs provide a high-level view of the organization’s overall health and progress towards long-term goals. Executives typically use them to gauge whether the company’s strategic objectives are being met.
Examples of strategic KPIs include return on investment (ROI), profit margin, and total company revenue. While they offer a snapshot of performance, they don’t dive deep into the specifics of what’s driving those numbers.
2. Operational KPIs
Where strategic KPIs zoom out, operational KPIs zoom in. These KPIs are focused on the short term and are much more granular. They track performance from month to month or even day to day, focusing on specific processes, product lines, or locations.
Operational KPIs are crucial for managers who need to monitor the efficiency and effectiveness of everyday operations. For instance, if company-wide revenue drops, operational KPIs help identify which particular areas are underperforming.
3. Functional KPIs
These KPIs are tailored to specific departments or functions within the organization. Each department uses functional KPIs to measure success relevant to their particular activities and responsibilities.
For example, the finance department may track new vendors registered in their system while the marketing team measures engagement metrics like click-through rates on campaigns. Functional KPIs can be strategic or operational but are designed to provide actionable insights for specific teams or departments.
Here’s a brief comparison of different types of KPIs with examples:
| Type of KPI | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative KPIs | Numerically measurable metrics. | Revenue growth, profit margins |
| Qualitative KPIs | Metrics based on qualities or descriptions are often subjective. | Employee satisfaction, customer testimonials |
| Leading KPIs | Indicators that predict future performance. | New leads, project milestones |
| Lagging KPIs | Indicators that reflect past results. | Historical financial results, customer retention rates |
| Input KPIs | Measure resources used for producing something. | Resources used, employee hours |
| Process KPIs | Focus on the efficiency or productivity of a process. | Throughput, compliance rates |
| Output KPIs | Measure the output or results of business activities. | Product output, services delivered |
| Practical KPIs | Track day-to-day operations to gauge immediate performance. | Daily active users, incident reports |
| Directional KPIs | Indicate the direction in which a company or market is moving. | Market trends, customer behavior |
| Actionable KPIs | Provide clear action points based on performance data. | Improvement targets, change management |
How to Set/Develop KPIs
Setting the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for tracking and enhancing your organization’s performance. It ensures that every metric you monitor directly contributes to your overall business goals.
1. Identify Business Objectives
Start by pinpointing what you really need to achieve.
For example, around 64 percent of businesses focus on tracking their marketing and sales pipeline as a KPI. This shows the importance of understanding your specific operational needs.
2. Align KPIs with Organizational Goals
Ensure your KPIs support your broader organizational goals.
For example, if your objective is to expand market reach, suitable KPIs could be new customer acquisition rates or market penetration percentages. This will help you accurately direct efforts and measure impact.
3. Define Clear and Measurable Targets and Determine Data Collection Methods
Set specific, quantifiable targets for your KPIs.
For instance, if your KPI is to increase customer retention, a clear target could be to improve retention rates by 10% within the next year.
Alongside this, decide on the tools and systems you will use to gather and analyze the data, ensuring that they can accurately and consistently measure the KPIs you’ve set. This preparation is key to effectively monitoring your progress.
4. Implement Tools And Software For Tracking
Leveraging the right tools and software is crucial for effectively tracking and managing KPIs, especially since 95% of HR leaders express dissatisfaction with traditional performance review systems, signaling a need for more dynamic, real-time KPI tracking methods.
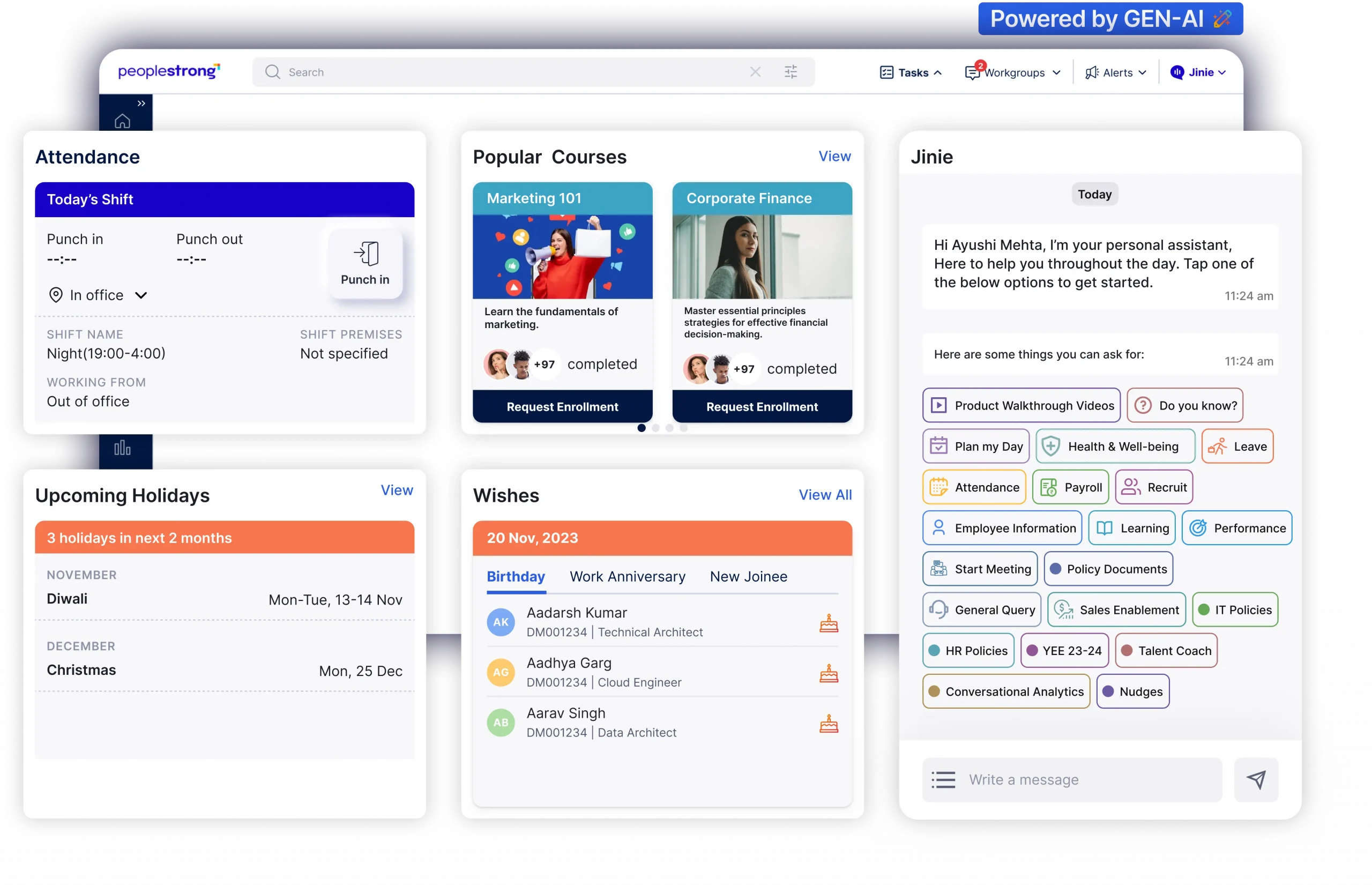
PeopleStrong, a comprehensive human resource management platform, offers robust features tailored for advanced KPI management. Here’s how it enhances KPI-oriented performance tracking:
- Configurable Goal Frameworks: With PeopleStrong, set up diverse goal frameworks like MBO (Management by Objectives) and OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) that align directly with specific KPIs, facilitating targeted performance tracking.
- Goal Management and Tracking: Easily create, track, and update individual or team goals across any device. This feature ensures all KPI-related goals are accessible and manageable from anywhere, enhancing real-time tracking capabilities.
- Automated Alerts and Notifications: Implement automated reminders to keep critical KPIs at the forefront of daily operations. This helps in maintaining focus on key metrics and ensures continuous monitoring.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Utilize structured feedback sessions that are essential for KPI analysis. Regular, actionable feedback helps refine KPIs and align them more closely with evolving business objectives.
- Performance Dashboards: Employ powerful dashboards that provide a comprehensive and real-time view of all performance metrics. These dashboards are crucial for visualizing KPI progress and making informed decisions quickly.
5. Adjust KPIs as Necessary Based on Performance and Feedback
As your business evolves, your KPIs should, too. Regular reviews of your performance metrics are crucial. If targets are consistently missed, this might signal that your KPIs are unrealistic or out of sync with current business conditions.
Additionally, feedback from team members can offer critical insights into necessary adjustments for enhanced accuracy and relevance.
How to Measure KPIs
Measuring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) effectively is all about keeping things precise and actionable. Here’s how you can nail it:
1. Define the data sources
First up, know where your data is coming from. This could be your sales figures, customer feedback, or even employee performance stats. Pinning down reliable data sources is crucial because you can’t measure what you can’t accurately track.
2. Collect data consistently
Consistency is key. Set a daily, weekly, or monthly routine for how often you’ll gather data. Stick to this schedule like glue because regular data collection ensures you have a continuous pulse on performance.
3. Utilize analytics software and tools
Here’s where tools like PeopleStrong come into play. These platforms make it a breeze to collect, analyze, and report data. With PeopleStrong, you can integrate data from different sources, track your KPIs in real-time, and even get automated insights that help you understand the numbers better.
4. Establish baseline measurements
Before you can improve, you need to know where you stand. Establish baseline measurements for each KPI to track progress over time. This is your starting point, and it’ll help you see just how far you’ve come.
5. Set performance targets
What’s your aim? Set clear, achievable targets for each KPI. These targets should challenge your team but remain realistic. They act as your north star, guiding all efforts and strategies.
6. Compare against targets and benchmarks
Finally, regularly compare your current data to your targets and industry benchmarks. This comparison tells you if you’re on track or if you need to pivot. It’s about making informed decisions that drive your business forward.
KPI Examples
Here are some examples of how different sectors can employ KPIs effectively:
1. Reduce Employee Turnover Rate
Measure: Annual turnover percentage
Target: Reduce employee turnover by 10% by the end of FY2023
Data Source: Human Resources Management System (HRMS)
Reporting Frequency: Quarterly
Owner: Head of Human Resources
Due Date: End of 2024
2. Boost Software Deployment Success Rate
Measure: Percentage of successful software deployments
Target: Increase deployment success from 85% to 95% by FY2023
Data Source: IT department deployment reports
Reporting Frequency: Monthly
Owner: IT Manager
Due Date: End of 2024
3. Improve Manufacturing Efficiency
Measure: Units produced per hour
Target: Increase production efficiency by 15% in FY2023
Data Source: Production line data
Reporting Frequency: Monthly
Owner: Plant Manager
Due Date: End of 2024
KPI Best Practices
Implementing KPIs effectively requires adherence to certain best practices to ensure they truly drive performance and inform strategic decisions. Here’s a guide to help you set up KPIs the right way:
1. Use the SMART Criteria
The SMART criteria lay the foundation for effective KPIs:
- Specific:Clearly define what each KPI will measure and why it’s important. The more specific your KPI, the easier it will be to understand and act upon.
- Measurable: Ensure that the KPI has a quantitative or qualitative measure to assess performance accurately.
- Achievable:The targets set for the KPI should be attainable within the resources, knowledge, and time you have.
- Relevant: Each KPI should be aligned with your organization’s strategic goals and objectives. If it doesn’t contribute to your end goals, it’s merely a distraction.
- Time-bound: Assign a clear timeline for achieving the targets specified by your KPIs. This could be monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the goal.
2. Involve Key Stakeholders
Stakeholder involvement at all levels—from executives to frontline employees—is crucial. By involving stakeholders in the development and ongoing review of KPIs, you ensure buy-in and relevance across the organization.
This collaboration also helps understand various perspectives and ensures that the KPIs are aligned with the needs of all parts of the organization.
3. Use a Mix of Leading and Lagging Indicators
To get a full picture of performance, use both leading and lagging indicators:
- Leading indicators predict future outcomes and can guide proactive adjustments. For example, the number of new leads can indicate future sales trends.
- Lagging indicators reflect the results of past actions, like quarterly sales figures, and are useful for confirming long-term trends. Balancing these indicators helps you manage your strategies’ immediate and long-term outcomes.
4. Leverage Data Visualization Tools for Clarity
Data visualization plays a crucial role in KPI tracking by making complex data easy to understand at a glance. Tools like PeopleStrong provide powerful visualization capabilities that allow you to create intuitive dashboards and reports.
These tools help you quickly grasp performance trends, comparisons, and patterns. For instance, PeopleStrong’s analytics platform can display data through various charts, graphs, and heatmaps, making it easier for teams to analyze their progress and make data-driven decisions.
As We Conclude
As businesses strive to navigate the complexities of modern markets, the use of key performance indicators (KPIs) has become indispensable. These metrics not only help track progress but also guide strategic decisions, ensuring organizations stay aligned with their goals.
However, the right tools are crucial for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting KPI data effectively, setting the stage for informed decision-making and sustained growth.
By leveraging advanced platforms like PeopleStrong, organizations can automate data collection, ensure real-time tracking, and gain actionable insights through intuitive analytics.
Ready to transform your KPI management?
Schedule a demo with PeopleStrong today and unlock your team’s full potential.